Aging DNA methylation
Gut microbiota promotes antigen presentation and immune response in intestines in both spatial- and temporal-dependent manner
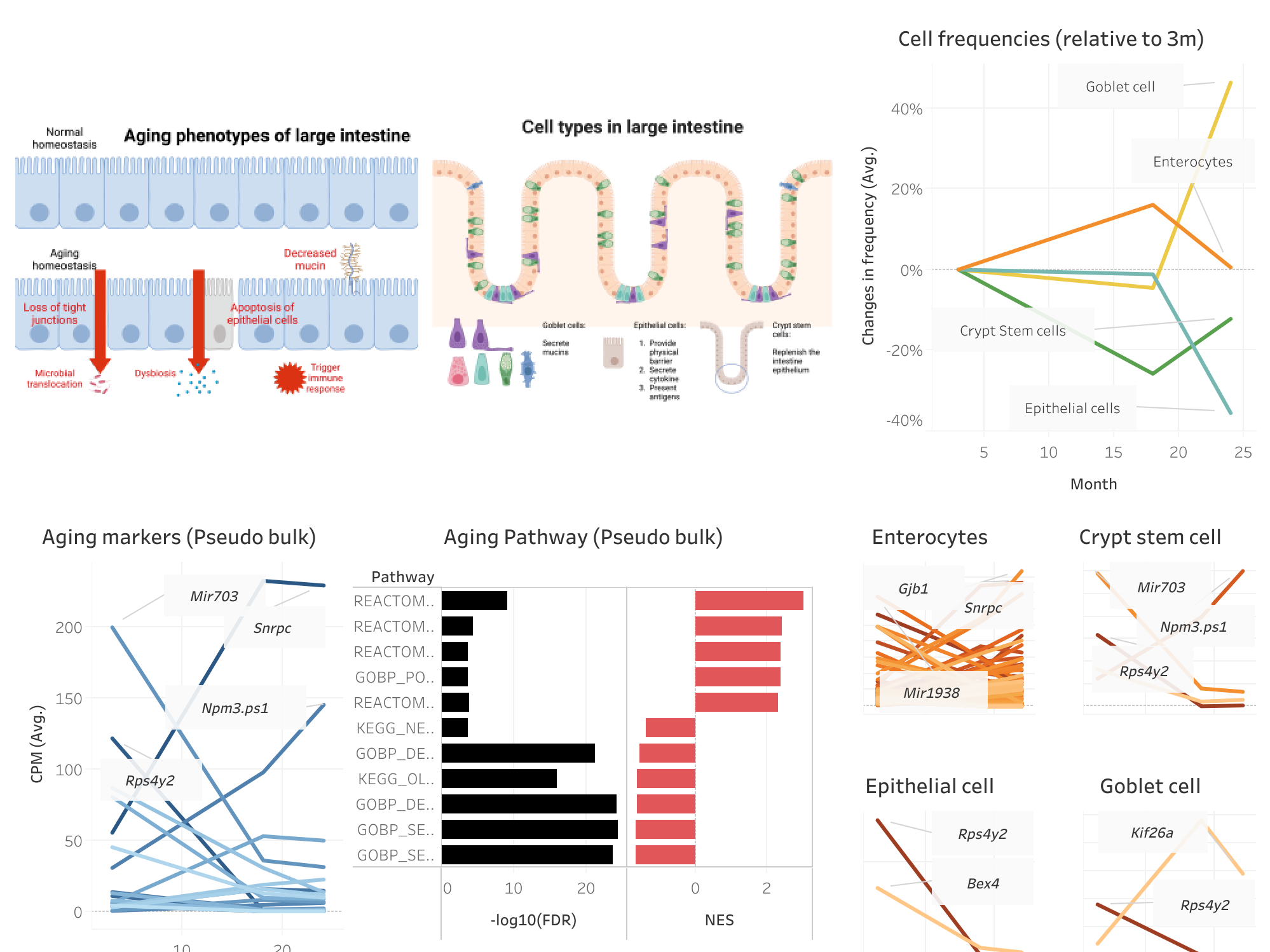
The mammalian intestinal tract is the largest immune organ and habitat for commensal microbes in the body. The distribution and composition of gut microbiota is not only heterogeneous along the intestinal tract but also dynamic throughout the aging process. However, how the temporal and spatial changes in gut microbiota affect intestinal immunity has not been well studied. To reveal the temporal and spatial complexity of microbial effects on intestinal immunity, we generated transcriptome profiles from small intestines, large intestines, and cecum from mice that have been maintained under specific-pathogen free (SPF) and germ-free (GF) conditions for 3, 17, and 78 weeks. We find that microbiota promotes immune response, particularly antigen presentation and T cell activation, in a both temporal- and spatial-dependent manner. Specifically, microbiota upregulates genes encoding major histocompatibility complex II (MHC II) and T cell receptor (TCR) signaling molecules only in small intestines and cecum of 78-weeks-old mice, not in 3- and 17-weeks-old mice. Moreover, by investigating the global methylation maps of intestines, we found genes encoding MHC II molecules are also associated with differentially-methylated regions (DMRs) between GF and SPF mice, suggesting microbiota regulate the expression of antigen presentation through DNA methylation. Together, our data provide the first insight of a genome-scale timeline of microbiota-dependent changes in DNA methylation and gene expression in mouse intestine.